DOMAIN • THREE
•KINgDOM protista•
Common name- Babesia divergens
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Apicomplexa
Class: Aconoidasida
Order: Piroplasmasina
Family: Babesiidae
Genus: Babesia
Species: divergens
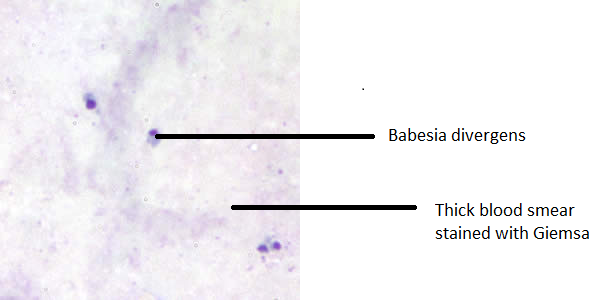
Figure 4b: Babesia divergens
This image shows a thick blood smear stained with Giemsa. The darker spots show the parasite.
Babesia divergens is a eukaryotic unicellular parasite which is found in red blood cells. This organism has flagellum and cilia which make it motile but it does not have a nervous system. It reproduces sexually by gametes and asexually by binary fission and it receives its nutrition by absorbing differentnutrients. This organism causes a disease which is transmitted by ixodid ticks. It is a disease that is mostly found in animals, but it can be naturally transmitted to humans. The disease is more severe and life threatening if the animal or human has no spleen. This is because the spleen is in charge of filtering the blood and replenishing the body’s supply of red blood cells. If there is no spleen, then the red blood cells cannot be cleansed of the disease. The disease is very rare and is most common in Europe. Babesia divergens has a pear shape when it is in the affected red blood cell [6b]. The chances of the host dying depend on the host’s resistance to the disease. Animals that live in places where the disease is more common will usually receive a mild case of the disease and recover with immunity. In addition, various drugs can be used to cleanse the blood of the parasites [7b]. This organism is chemoheterotrophic, meaning it obtains its energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environment.
Why this belongs in this Domain:
Babesia divergens belongs in this domain for a few reasons. It contains a nucleus but it does not contain a nervous system. Also, Babesia divergens moves around using flagella and cilia. This organism reproduces sexually, by gametes, and asexually, by binary fission. Because of this, it is shown that this organism belongs in this phylum, Apicomplexa. It does not belong in domain Archaea or domain Bacteria because it is a eukaryote.
Common name- Trypanosoma brucei
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Euglenoza
Class: Kinetoplastea
Order: Trypanosomatida
Family: Trypanosomatidae
Genus: Trypanosoma
Species: brucei
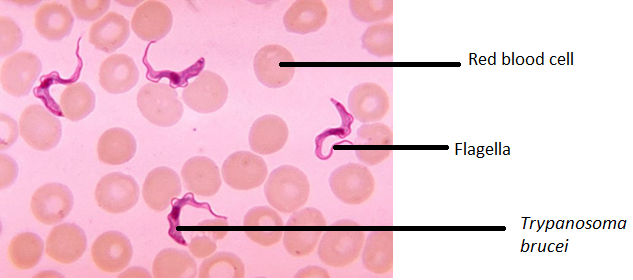
Figure 5b: Trypanosoma brucei
This image shows a smear of blood with red blood cells and Trypanosoma brucei.
Trypanosoma brucei is a unicellular eukaryotic cell that measures 8 to 50 μm in length. It has a long body and contains many organelles similar to those in a human body, however, it does not have a nervous system. This organism is motile via flagellum. They are connected to the cytoskeleton of the cell’s body. Similar to many other organisms in domain Eukarya, the Trypanosoma brucei is chemoheterotrophic meaning it receives its energy by the oxidation of electron donors in the surrounding environment. Trypanosoma brucei is found where there are many tsetse flies in tropical and subtropical areas of Africa. It can reproduce asexually through binary fission, or it can reproduce sexually by gametes [8b]. In order for it to be able to reproduce, it needs two hosts. Its life cycle begins when a tsetse fly bites human skin. The parasite, Trypanosoma brucei enters the bloodstream and starts to multiply. However, the immune system does not kill this parasite because it has a glycoprotein coat which makes it difficult for the body to recognize [9b].
Why this belongs in this Domain:
This parasite belongs in this domain because it is a chemoheterotroph and all protists are either phototrophs or chemoheterotrophs. It belongs in the phylum Euglenozoa because it has flagella and is a protozoa. Since it only has one flagellum it belongs in the order Trypanosomatida. Also, it can reproduce sexually or asexually. Although it can reproduce in more than one way like organisms in domain Archaea, this organism does not belong there because their modes of nutrition differ. Even more so,Trypanosoma brucei does not belong in domain Bacteria because it has eukaryotic cells, not prokaryotic .
RJ